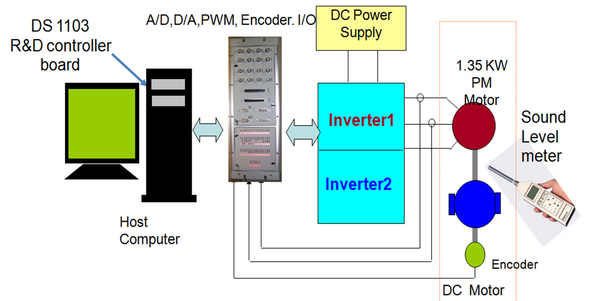
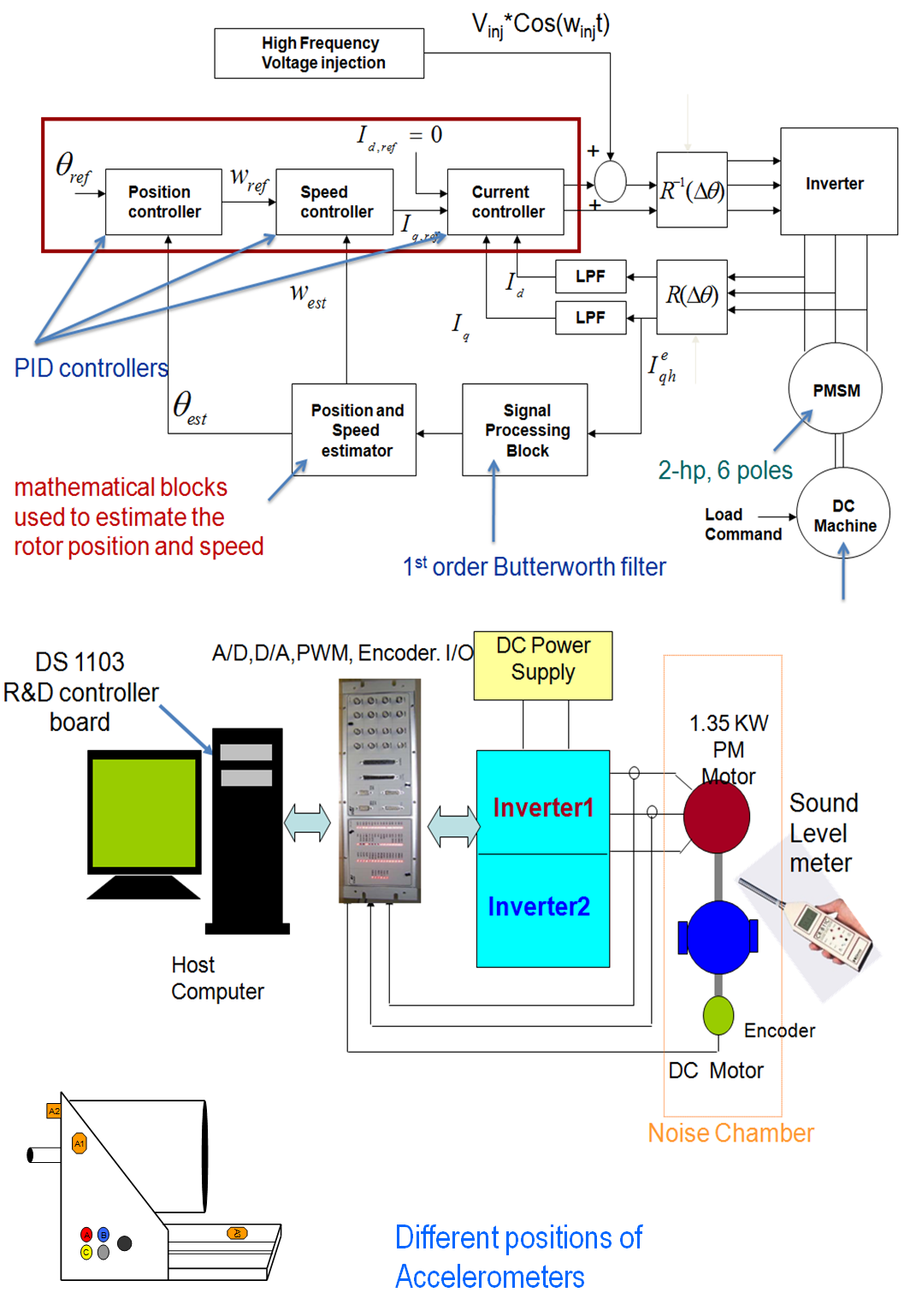
Objectives of Paper:
- Reduction of vibration
- reduction of acoustic noise
Sensorless control of PMSM at low speed:
- Motor is excited by fluctuating voltage carrier signal Vinj Cos(wt)
- High frequency impedance is measured.
- Excitation signal is injected in stationary reference frame
- Based on inductance variation due to rotor saliency.
How is it Done:
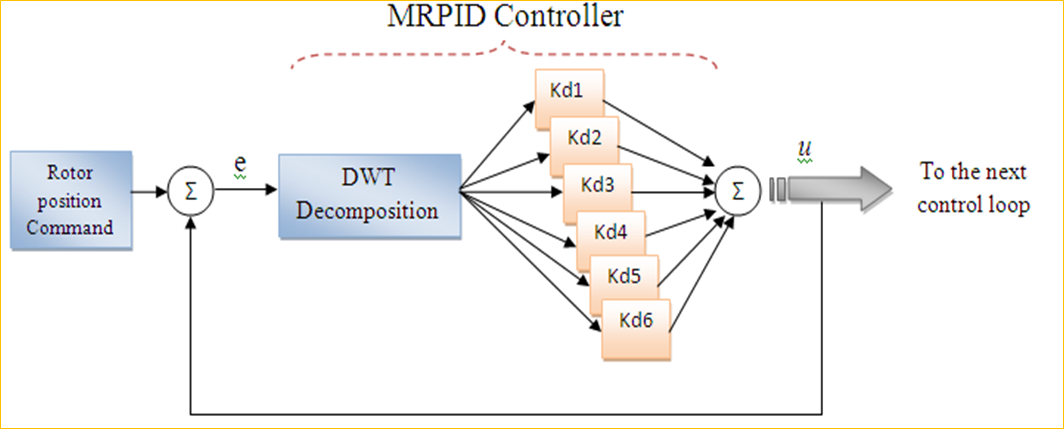
Multi-Resolution Controller:
- The use of wavelet transform
- Error Signal decomposition
Parameters tuning:

Online optimization problem formulation:
Gains ![]() are used to tune high and medium frequency components of the error signal
are used to tune high and medium frequency components of the error signal
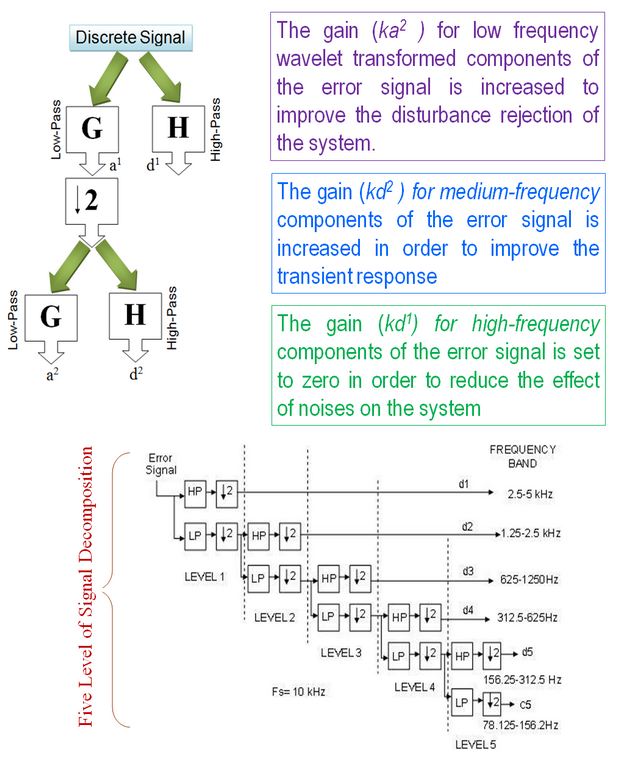
Online optimization problem formulation:
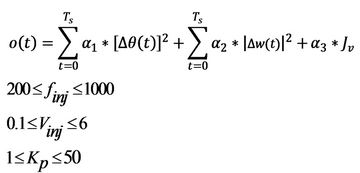
0.01< {Kd1, Kd2, Kd3} <10
How Jy is calculated?
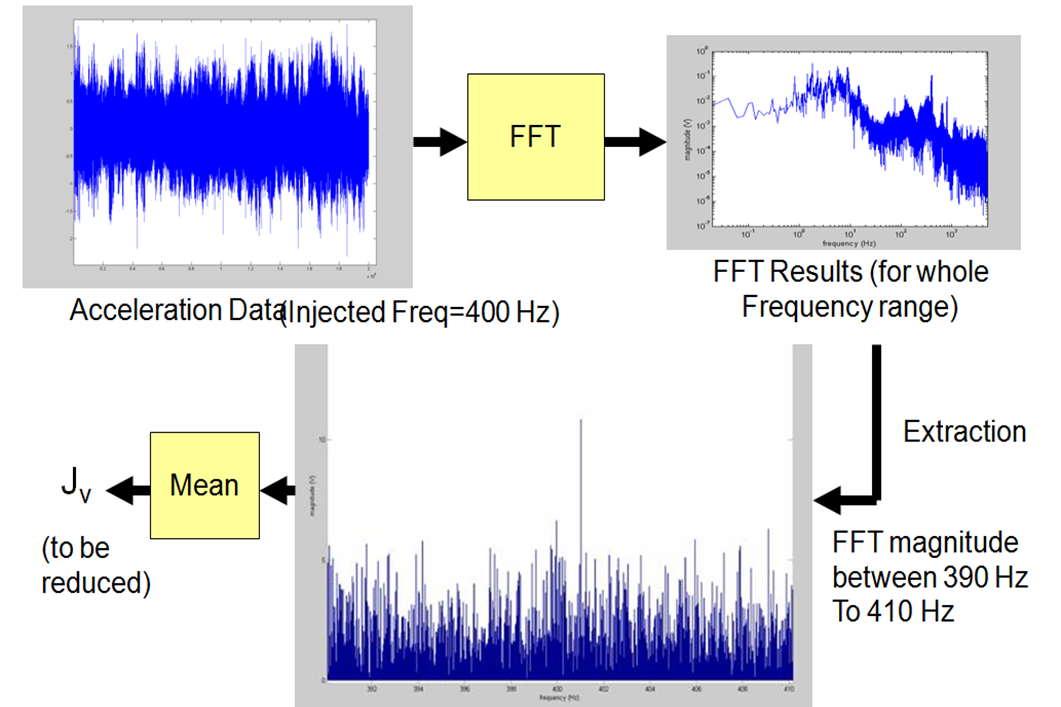
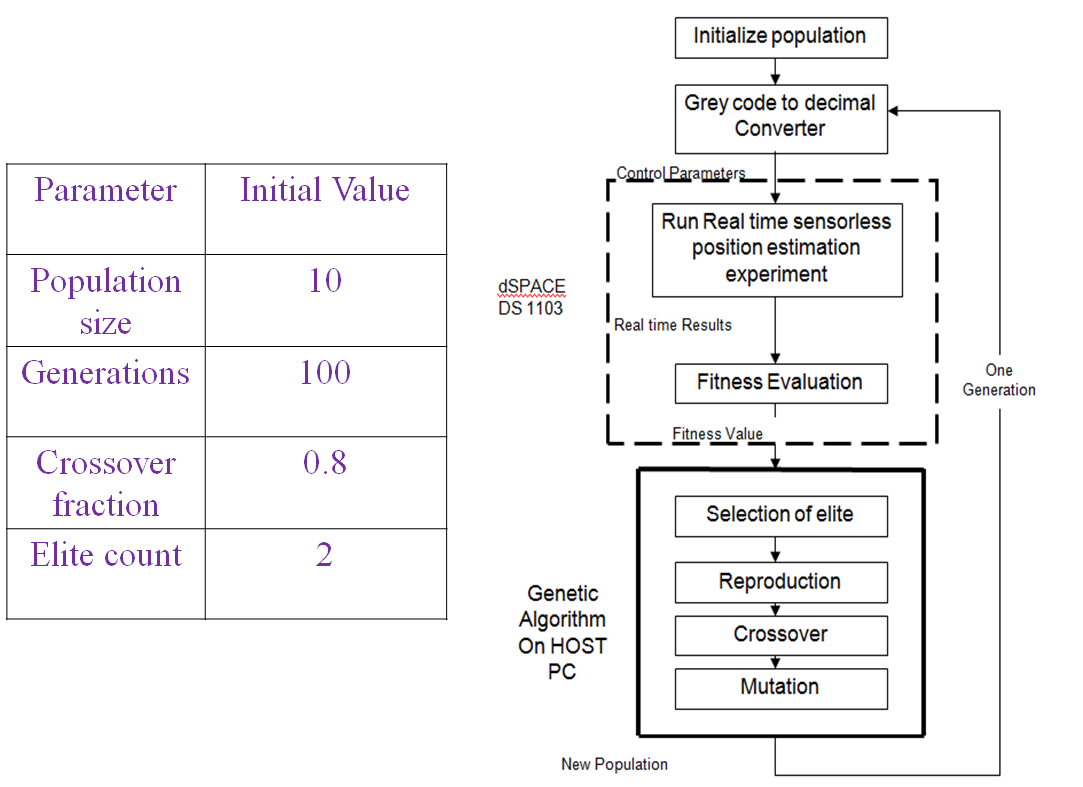
Procedure of Optimization with hardware in the loop:
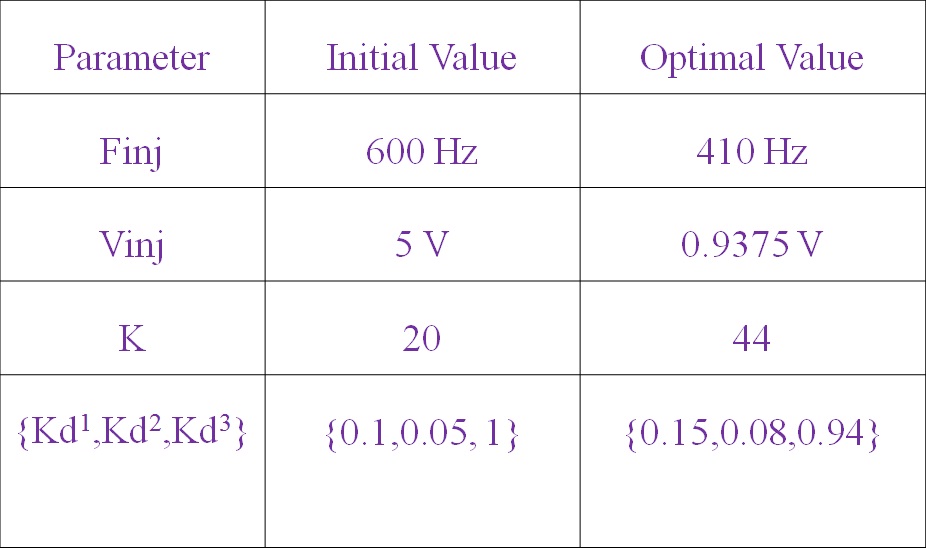
Optimization Results:
Experimental Results:
Speed controller response to a step change in the reference speed from 10 to 30 deg/sec
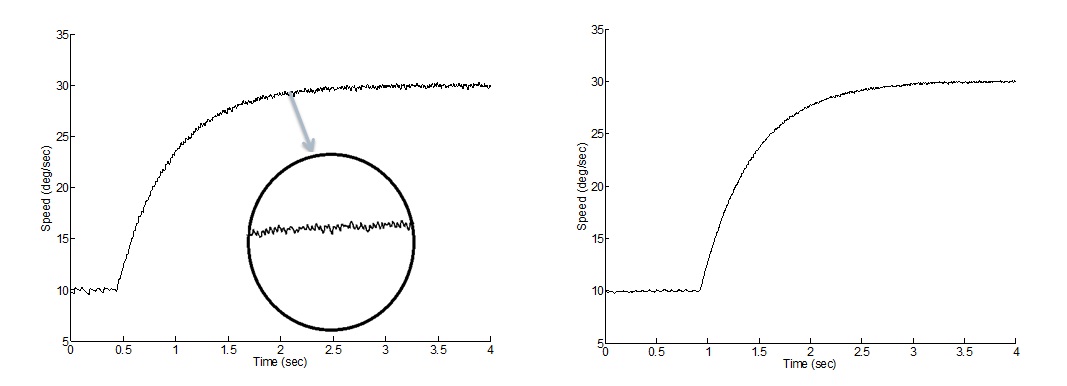
fig: Before optimization fig: After optimization
FFT Analysis of the Accelerometer Results:
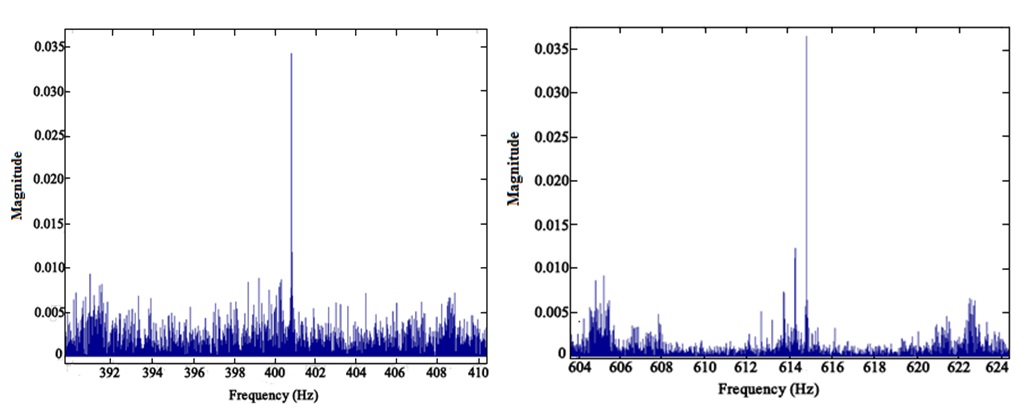
fig: Axial vibration before optimization fig: Axial after optimization
Noise Measurements of the PM Motor using Axial & Radial Accelerometer:
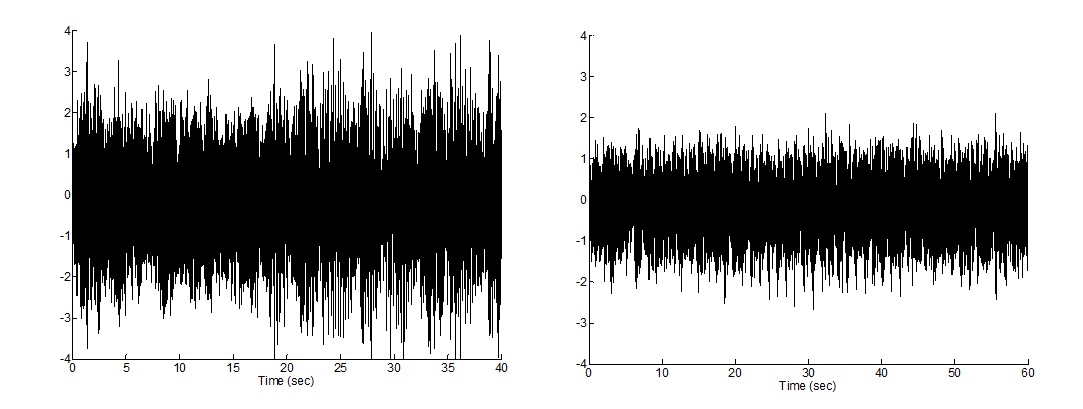
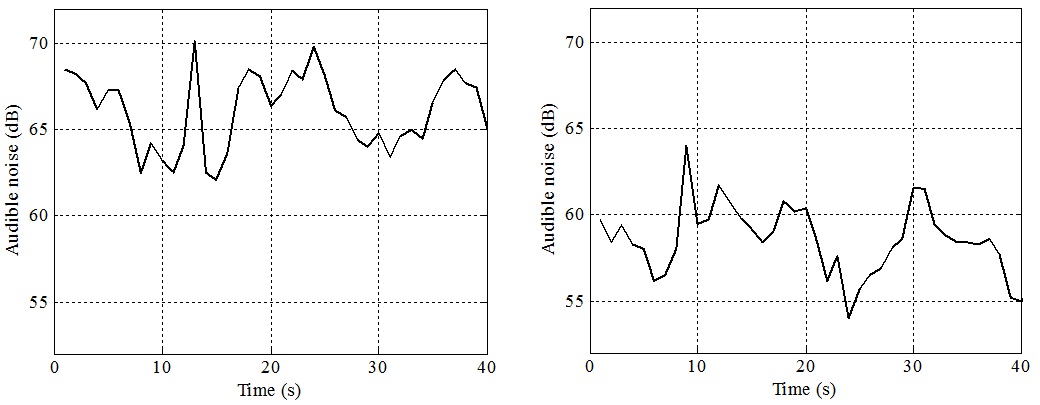
Audible Noise Measurement:
Conclusion:
- Axial & Radial Vibration are reduced (up to 10%)
- Steady state Error is reduced (up to 5%)
- Smooth operation of the motor is obtained
- Motor produces less amount of audible noise (up to 18%)