Introduction:
- Applying DC distribution in shipboard power systems has acquired the attention of the U.S Navy as an alternative to conventional AC systems.
- The vast increase of load demand and the need to a high reliability high quality power supply to feed such loads are the main reasons for this.
- Moreover, there is a great leap towards the utilization of sustainable energy sources. Fuel cells seem to be the most convenient sustainable energy sources onboard of a ship.
- In this paper, integration of fuel cells energy into DC zonal electric distribution systems (DC ZEDS) has been investigated. Different power electronic topologies have been proposed and validated.
DC Zonal Electric Distribution Systems:
- A grid connected DC distribution system.
- The system is divided into zones that facilitate the protection of the system.
- The fuel cells energy is typically integrated using conventional boost converters with the output capacitor eliminated.
- This topology yields a pulsating output current, which means poor power quality.
Conventional Boost Converter:

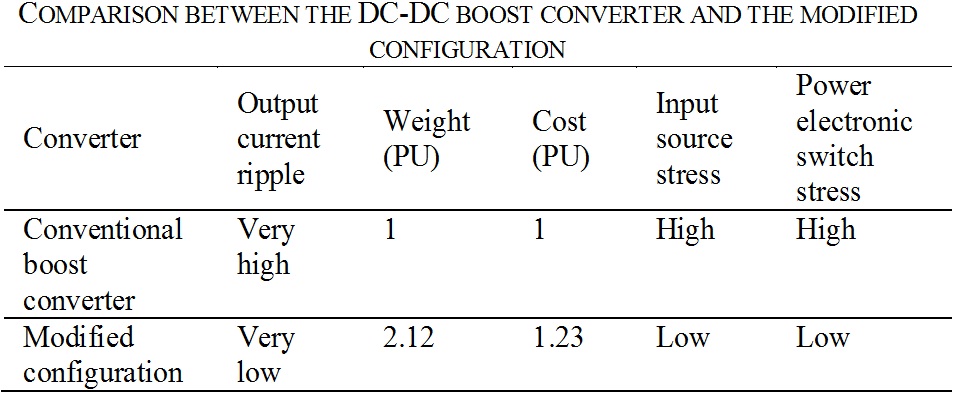
Modified Boost Converter Topology:
- The conventional boost converter is modified by adding an output LC-filter.
- The modified topology assures constant output current.
- Using this converter, the instantaneous value of the current can be controlled rather than its average as in the case of conventional boost converters.

Mechanical Modeling of the Proposed Converter:

Results of the Proposed Topology:

fig: This converter supplies continuous output current
Application of the proposed topology for power sharing among different sustainable energy sources connected to a common DC bus:
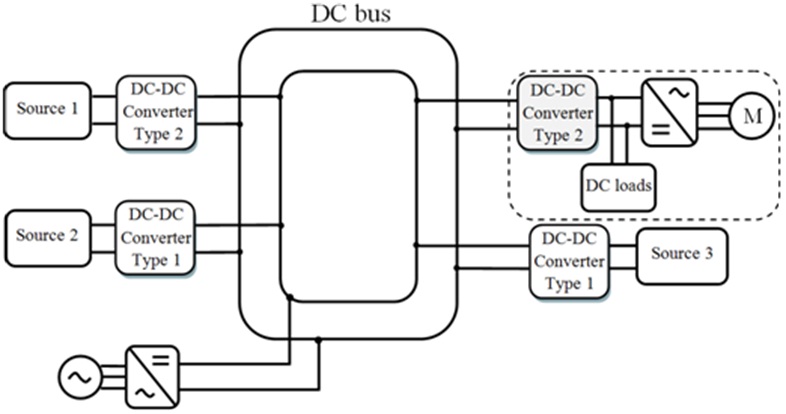
- One of the three DC-DC converters is a DC-DC boost converter (Type 2) used to regulate the voltage on the DC bus and is free to supply the power required in the network.
Results of the power sharing:
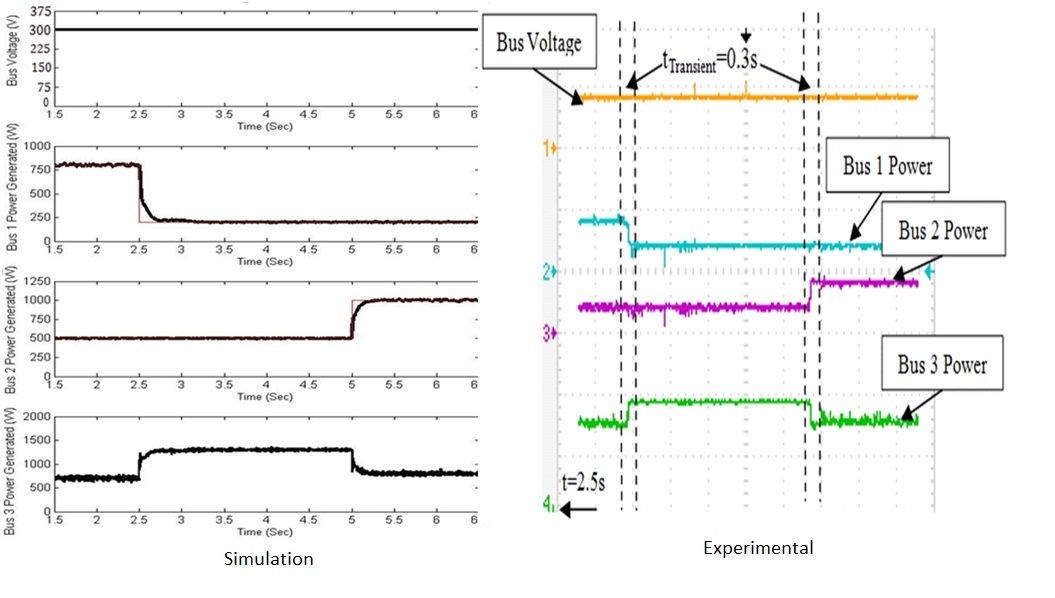
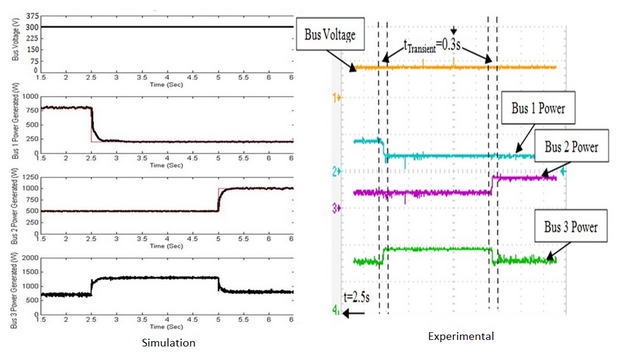
- Power sharing response to a step change in the power reference
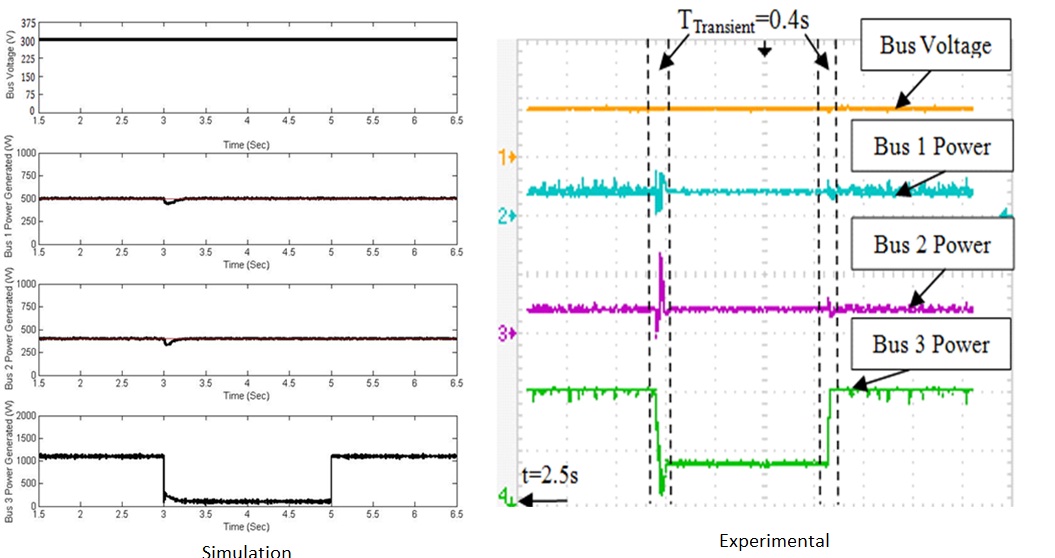
- Power sharing response to a step change in load demand
Conclusion:
- In this paper, the application of DC-DC boost converters as an interface between fuel cells and the DC bus in a DC zonal electric distribution system (DC ZEDS) have been investigated.
- Investigating the performance of the conventional DC-DC boost converter, it has been found that yields a pulsating output current, which is not convenient for ship board applications.
- A modification has been applied to it in order to enhance its performance. The proposed converter’s performance has been compared to that of a conventional boost converter.
- The application of the proposed topology for power sharing in DC distribution network has been also investigated.
- Both simulation and experimental results verifies the validity and applicability of the proposed topology.