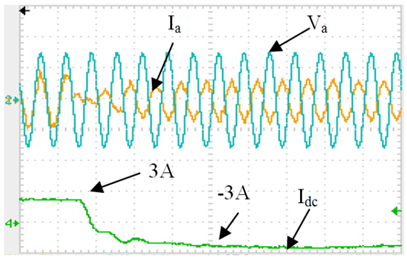
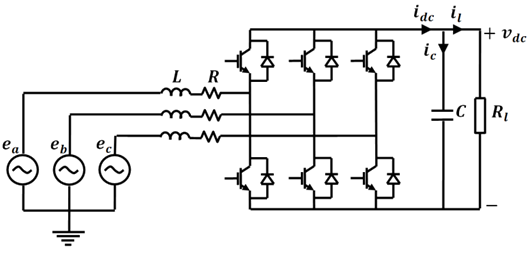
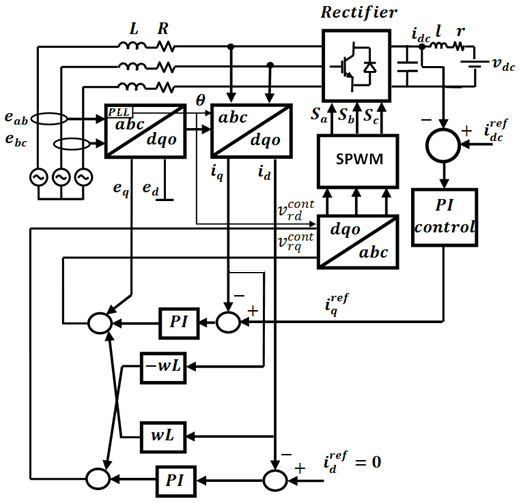
In this area of research, some of the aspects related to the connectivity of DC microgrids to the main grid are investigated. A prototype system has been designed and implemented to address these aspects. The described system is dependent mainly on sustainable energy sources. Hence, a special care has been given to dealing with this kind of sources while designing different components of the system. Certain features had to be maintained in the system in order to assure efficient integration of different sources such as, efficient and reliable load-feeding capability and full controllability of voltage and power flow among various buses in the system. Two different converters have been investigated; firstly, a fully controlled rectifier has been designed to tie the DC grid with the AC one. A vector decoupling controlled sinusoidal pulse width modulation (SPWM) technique has been used to allow the designed rectifier to maintain a constant output voltage while being able to control the active and reactive power drawn from the grid independently. Hence, this controlled rectifier acts as a voltage regulator for the DC microgrid and has a uni-directional power flow capability from the AC grid to the DC microgrid. Moreover, in order to allow bi-directional power flow, a bi-directional AC-DC/DC-AC converter has also been designed. The Bi-directional AC-DC/DC-AC converter controls the active power transferred from the DC grid to the AC grid while operating at unity power factor. In addition, it controls the active power transferred from the AC grid to the DC grid while operating at unity power factor. Both simulation and experimental results verify the validity of the proposed system.